Summarize
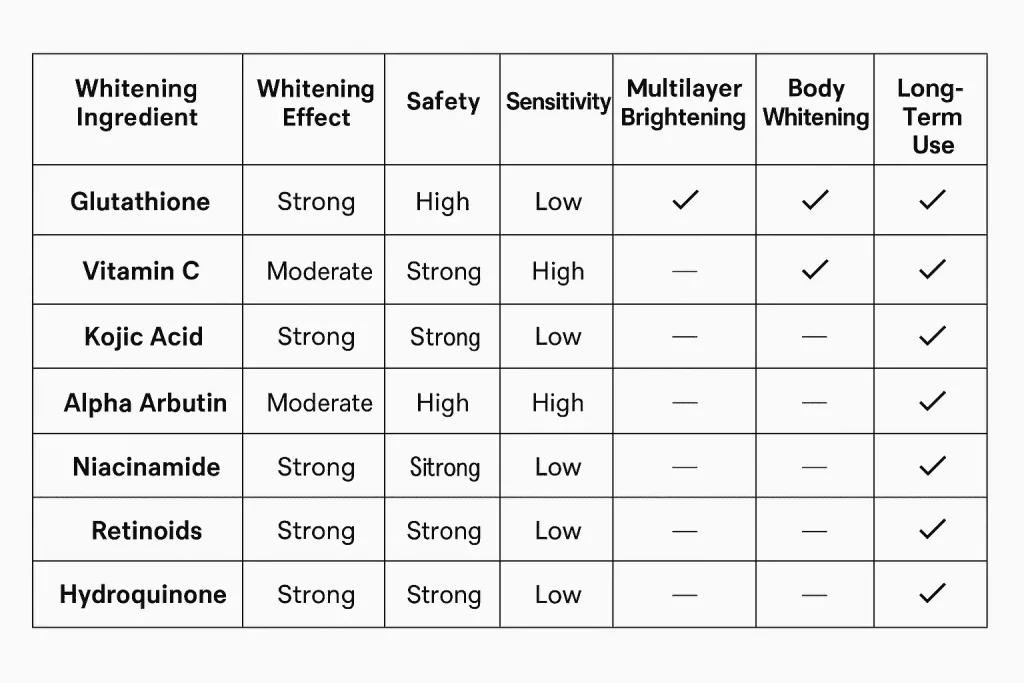
Glutathione is one of the most effective antioxidants used for skin whitening and pigmentation reduction, but how does it compare to other popular whitening ingredients such as Vitamin C, Kojic Acid, Alpha Arbutin, Niacinamide, and retinoids? This guide provides a detailed ingredient-by-ingredient comparison to help understand which brightening method works best, who it is suitable for, and how it performs against stubborn pigmentation such as melasma, tanning, acne marks, and dark patches.
Introduction
With the rising concern of skin tanning, dark spots, dullness, and melasma in regions with strong sunlight like Pakistan, whitening and brightening ingredients have become a major part of skincare routines. While Glutathione has gained massive popularity for its safe and long-lasting brightening effects, many people want to know how it compares to other ingredients commonly used for skin whitening.
This in-depth guide compares Glutathione with the most popular whitening ingredients, explains their strengths and limitations, and clarifies which ingredient is best for different skin concerns. Every comparison is based on mechanism, science, usage, and long-term results.
What Makes Glutathione Unique?
Glutathione is different from other whitening ingredients because it works internally and externally. Most ingredients lighten the skin by reducing surface pigmentation, but Glutathione works deeper by:
- Reducing melanin production
- Shifting dark melanin (eumelanin) to light melanin (pheomelanin)
- Repairing UV-damaged skin cells
- Detoxifying the body
- Improving skin clarity from the inside
This dual action makes it more effective for full-body whitening, whereas most other brightening ingredients only work on the face or surface-level pigmentation.
How Glutathione Works for Whitening
Glutathione reduces pigmentation through three major mechanisms:
Inhibiting Tyrosinase Activity
Tyrosinase is the key enzyme responsible for melanin production. When melanin is reduced, skin naturally becomes lighter and brighter.
Converting Dark Melanin to Light Melanin
Glutathione reduces the production of dark melanin (eumelanin) and promotes lighter melanin (pheomelanin), leading to fairer skin. Glutathione helps reduce dark spots and uneven pigmentation.
Deep Antioxidant Action
It neutralizes free radicals caused by sunlight, pollution, and stress—major contributors to dark spots and rough texture.
Detoxification
A cleaner internal system results in a clearer, brighter complexion.
Because of its multi-layer action, Glutathione provides brightening that is more uniform, long-lasting, and natural looking.
Comparison With Other Whitening Ingredients
Glutathione vs Vitamin C
How Vitamin C Works
Vitamin C brightens skin by reducing melanin, boosting collagen, and repairing sun damage. It improves glow and overall skin clarity.
Strengths
- Excellent for glow
- Repairs damaged skin
- Boosts Glutathione effectiveness
- Strong antioxidant
Limitations
- Can irritate sensitive skin
- Does not lighten deep melasma alone
- Does not provide full-body whitening
Which Is Better?
For whitening: Glutathione
For glow & antioxidant: Vitamin C
Best results: Use both together
Glutathione vs Kojic Acid
How Kojic Acid Works
Kojic Acid blocks tyrosinase and is effective for deep pigmentation, especially melasma and brown patches.
Strengths
- Strong for melasma
- Works well for dark spots
- Good for stubborn pigmentation
Limitations
- Can irritate sensitive skin
- Not suitable for daily use in high concentrations
- Works only on the surface
Which Is Better?
For overall whitening: Glutathione
For melasma spots: Kojic Acid
Best results: Glutathione + Kojic Acid night routine
Glutathione vs Alpha Arbutin
How Alpha Arbutin Works
Alpha Arbutin gently reduces melanin production and is known for its safe, long-term brightening effect.
Strengths
- Very gentle
- Safe for all skin types
- Works well for uneven tone
- Ideal for long-term use
Limitations
- Works slower than Glutathione
- Only surface-level brightening
- Not strong enough for deep pigmentation alone
Which Is Better?
For fast results: Glutathione
For sensitive skin: Alpha Arbutin
Best results: Glutathione + Alpha Arbutin combination
For a gentle but effective topical brightening option, many users prefer the Glutaone Skin Brightening Serum, available at Glutapro.com.
Glutathione vs Niacinamide
How Niacinamide Works
Niacinamide brightens by reducing melanin transfer and repairing the skin barrier.
Strengths
- Great for redness
- Controls oil
- Reduces acne marks
- Strengthens skin barrier
Limitations
- Results take time
- Mild whitening effect
- Works best with other actives
Which Is Better?
For whitening: Glutathione
For barrier strengthening: Niacinamide
Best results: Glutathione + Niacinamide morning routine
Glutathione vs Retinoids (Retinol)
How Retinoids Work
Retinol increases cell turnover, fades pigmentation, and reduces fine lines.
Strengths
- Excellent for anti-aging
- Improves texture
- Reduces pigmentation
Limitations
- Can irritate the skin
- Requires strict sun protection
- Not suitable for beginners
- Does not lighten the whole face evenly
Which Is Better?
For whitening: Glutathione
For aging + pigmentation: Retinol
Best results: Retinol at night + Glutathione (topical or oral)
Glutathione vs Hydroquinone
How Hydroquinone Works
Hydroquinone stops melanin production aggressively and is used for severe melasma. Glutathione supports melasma improvement by reducing melanin overproduction.
Strengths
- Strongest pigment reducer
- Works fast
- Effective for stubborn melasma
Limitations
- High irritation risk
- Not recommended long-term
- May cause rebound pigmentation
- Can cause skin thinning
- Banned in many countries
Which Is Better?
For safe long-term whitening: Glutathione
For dermatologist-supervised melasma treatment: Hydroquinone
Best results: Glutathione for maintenance after Hydroquinone
Glutathione vs Chemical Peels (AHA/BHA)
How Chemical Peels Work
They exfoliate the top layer and reduce pigmentation.
AHA like Glycolic Acid help exfoliate the top layer and reduce pigmentation.
Strengths
- Fast exfoliation
- Good for dullness and acne marks
- Smooths texture
Limitations
- Temporary results
- May cause sensitivity
- Not suitable for long-term daily use
Which Is Better?
For long-term whitening: Glutathione
For quick surface clarity: AHA/BHA
Best results: Peels occasionally + Glutathione daily
Which Ingredient Works Best for Which Concern?
For Whitening
- Glutathione
- Vitamin C + Glutathione
- Alpha Arbutin
For Melasma
- Kojic Acid
- Glutathione
- Niacinamide
For Dark Spots
- Glutathione
- Alpha Arbutin
- Glycolic Acid
For Acne Marks
- Glutathione. Glutathione works well for acne marks and post-inflammatory pigmentation.
- Niacinamide
- Salicylic Acid
For Glow
- Vitamin C
- Glutathione
- Hyaluronic Acid
For Anti-Aging
- Retinol
- Vitamin C
- Glutathione
You can buy original, dermatologist-approved Glutathione products directly from our official store: Glutapro.com.
How to Combine Glutathione With Other Ingredients
The most effective whitening combinations are:
Glutathione + Vitamin C
Enhances antioxidant power; brightens faster.
Glutathione + Alpha Arbutin
Safe and gentle; good for long-term whitening.
Glutathione + Niacinamide
Improves tone and skin barrier.
Glutathione + Kojic Acid
Targets deeper melasma and dark patches.
Glutathione + Hyaluronic Acid
Improves hydration and healing.
Safety Comparison
Here is the safety ranking (1 = safest):
- Glutathione
- Hyaluronic Acid
- Niacinamide
- Vitamin C
- Alpha Arbutin
- Kojic Acid
- AHA/BHA
- Retinoids
- Hydroquinone
Glutathione remains one of the safest long-term brightening ingredients .For authentic Glutathione serums, creams, and supplements manufactured by Zonex Pharma, visit: Glutapro.com.
Who Should Use Glutathione?
Glutathione is suitable for adults of all skin types who struggle with tanning, dullness, pigmentation, or uneven skin tone. It is equally effective for men who work outdoors and face sun-induced darkening, as well as women dealing with long-term pigmentation and melasma. Anyone looking for a safe, long-term brightening solution can benefit from Glutathione.
If you want to learn more about the science behind each brightening ingredient, visit our complete Ingredients Guide: Ingredients Library
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Glutathione better than other whitening ingredients?
For full-body whitening and long-term results, yes.
Can Glutathione be combined with all ingredients?
Yes, it is safe with Vitamin C, Niacinamide, Arbutin, HA, Kojic Acid, and AHA/BHA.
Does Glutathione work for deep pigmentation?
Yes, especially when combined with Kojic Acid or Alpha Arbutin.
How long does Glutathione take to show results?
Four to twelve weeks depending on skin type.
Which ingredient is the strongest?
Hydroquinone is strongest but not safe long-term. Glutathione is safest.


